SEO Google - Optimization Guide in Web Search Engines
Search Engine Optimization often consists of modifications that could have an impact on the user experience and site performance.

Search engine optimization often consists of small modifications to specific parts of your website.
When these modifications are considered individually, they can be perceived as improvements, but when combined with other optimizations, they could have a big impact on the user experience and site performance in organic search results.
Create unique and precise page titles
Indicate the titles of the pages using the title labels
A title label indicates both the users and the search engines the subject on which a page deals.
The <title> tag must be placed inside the <head> tag in the HTML document. Ideally, create a unique title for each page of the site.

The title of the home page of our baseball sticker site, which lists the name of the company and the three areas it focuses on.
The content of the title tag is displayed in the search results
If the document appears on a search results page, the content of the title tag usually appears on the first line of the results.
If you are not familiar with the different parts of a Google search result, you can take a look at the following video by title "Anatomy of a search result".
The words in the title will appear in bold if they are the same words as the words of the user's search. This can help users recognize if the page is relevant to their search.
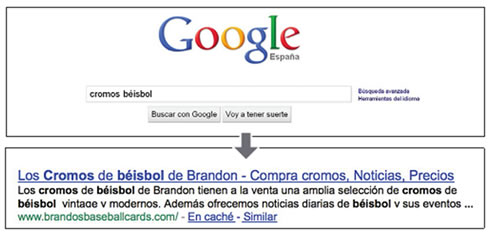
Un usuario realiza la consulta [cromos béisbol]. La página principal se muestra como resultado, con el título en la primera línea (ten en cuenta que las palabras de la consulta que el usuario buscó aparecen en negrita).
A user performs the query [baseball cards]. The main page is shown as a result, with the title on the first line (keep in mind that the words of the query that the user searched appear in bold).
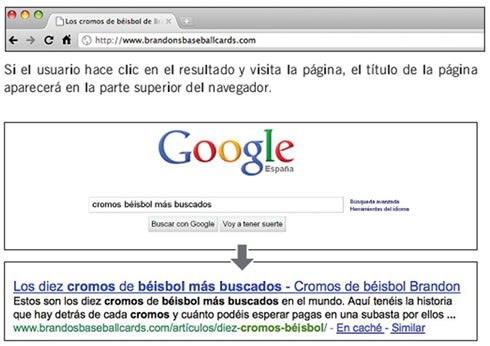
A user makes the query the query [most wanted baseball cards]. A relevant internal page (whose title is unique to the content of the page) of our website appears as a result.
It is recommended to have a length between 60 and 64 characters.
Recommended practices
Describe precisely the content of the page
Choose a title that clearly indicates the theme of the page
Avoid:
- A title that has no relation to the content of the page
- The use of default or too generic titles such as "Untitled" or "New Page"
Create unique title tags for each page
Ideally, each of your pages has a unique title tag, which helps Google distinguish that page from the rest of pages on your site.
Avoid:
- The use of a single label for all the pages of your site, or for many of them
Use short descriptive titles
The titles can be concise but informative. If the title is too long, Google will show only a part of it in the search result.
Avoid:
- Very long titles that are not useful for users
- Fill title tags with unnecessary keywords

Use the meta tag description
The texts can be defined for each page
The meta description of a page provides Google and other search engines with a summary on the page.

The meta tag description on our home page offers a brief overview of the site.
While the title of a page contains a few words, the description meta tag could contain a couple of sentences or even a short paragraph.
Like the <title> tag, the description meta tag is placed inside the <head> tag in the HTML document.
What are the advantages of the description goals labels?
The description meta tags are important since Google could use them as description fragments of your pages.
On the other hand, Google may choose to use a relevant part of the visible text of your page if it matches the user's query.
Add meta tags description for each of your pages is always a good practice in case Google cannot find a good text to use as a fragment.
The words that appear in the fragment are in bold if they match the user's query.
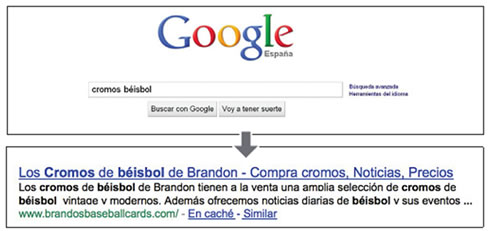
A user performs the query [baseball cards]. Result of the main page with a fragment of the meta tag description.
This gives clues to the user to know if the content of the page matches what he is looking for.
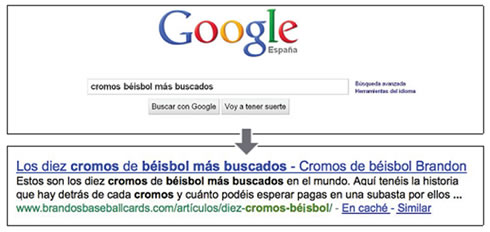
A user performs the query [most wanted baseball cards]. One of the internal pages, with its unique meta description used as a fragment, appears as a result.
It is recommended to have a length between 150 and 160 characters.
The description should be brief, many search engines only show the first 150 or 200 characters. Even if it were possible to include more extensive texts you should remember that users usually take a look at the search results rather than stop to read them in detail.
Recommended practices
Accurately summarize the content of the page
Write a description that reports and in turn creates interest in the users in case you find that description meta tag as a fragment of a search result.
Avoid:
- A meta tag description with content not related to the page
- Generic descriptions like "This is a Web page" or "Page on baseball cards"
- A description with only keywords
- Copy and paste all the content of the document into a meta tag description
Use unique descriptions for each page
Having a different meta tag for each page helps both users and Google especially in searches where users can obtain multiple pages from your domain (for example, searches with the site operator :)
If your site has thousands or even millions of pages, making meta tags by hand will not be feasible. In this case, they can be generated automatically based on the content of each page.
Avoid:
- Use a single meta tag description on all pages of your site or in a large group of pages on your site

keywords
When it comes to showing results there are search engines that accompany the reference with information obtained from the page itself instead of writing an automatic or manual summary. This indicates the importance of including information in the metatags of the page, since this will be the information that potential users will have about our page when viewing it in the search engines.
The list of keywords is usually not displayed on the results page, but sometimes determines the ranking.
You must include synonyms, acronyms, and in general terms that may be included in the user's search strategy.
The study of search expressions issued by users is one of the most useful tools to approach the real needs or interests of users, and logically act accordingly.
Improve the URL structure
Single URL suggest the content of the page
Creating descriptive categories and file names for your website documents can not only help keep your website better organized, it could also facilitate the tracking of your documents to the search engines.
In addition, you can create simpler URLs to link. Users who visit your site may feel intimidated by very long and rare URLs, with few recognizable words.
URLs of this type can be confusing.
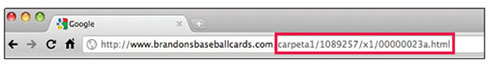
A URL that points to a page on our site that our users might have difficulties with.
It would be difficult for users to repeat the memory URL or link it. In addition, users may believe that a part of the URL is not necessary, especially if the URL shows many unrecognizable parameters. They could leave out a part, thus breaking the link.
Some users could link to your page using the URL of the page as anchor text.
If the URL contains relevant words, it provides users and search engines with additional information about the page beyond what would be given by a session ID or a parameter name.

The highlighted words could inform the user or the search engine about the page even before clicking on the link.
URLs are displayed in search results
Finally, remember that the document URL is displayed as part of a Google search result, after the title of the document and the descriptive snippet.
Like the title and the snippet, the words in the URL of the search result will appear in bold if they match the user's query.

A user performs the query [baseball cards]. Our main page appears as a result, with the URL under the title and the fragment.
On the right there is another example that shows a URL of our domain for a page that contains an article about most wanted baseball cards.
The words in a URL are more attractive to users than options such as:
"www.brandonsbaseballcards.com/articulo/102125/".
Google is good at tracking all kinds of URL structures, even if they are very complex, but creating URLs as simple as possible, both for users and for search engines, can be very useful.
Some Webmasters rewrite dynamic URLs as static URLs. This is an advanced procedure and, if done incorrectly, could cause problems.

Recommended practices
Use words in URL
URLs with words relevant to the content and structure of the site to help users visiting your site navigate through it.
They will remember them better and can facilitate that they link to them.
Avoid:
- Long URLs with parameters and unnecessary session identification numbers
- Generic names like "pagina1.html"
- Excessive use of keywords such as "baseball-chromos-baseball-chromos-baseballs.html"
Create a simple directory
Structure Use a structure of directories that organize the content and provide the users who visit your site to know where they are inside it..
Try using the directory structure to indicate the type of content found in that URL.
Avoid:
- Naming subdirectories such as "../dir1/dir2/dir3/dir4/pagina.html"
- Names of directories without any relation to the content
Provide a version of the URL to reach a document
To prevent users from linking to a version of the URL and other links to a different version (this could divide the content's reputation between the two URLs), focus on using and referring a URL in the structure and in the internal links of your pages.
If you notice that users access the same content through several URLs, you can create a redirect 301 from non-preferred URLs to the dominant URL.
You can also use the canonical URL or the link element rel = "canonical" if you can not redirect.
Avoid:
- Which pages from subdomains and from the root directory access the same content (for example, "dominio.com/pagina.html" and "sub.dominio.com/pagina.html")
- Use unnecessary capitalization in URLs (many users they wait for lowercase URLs and remember them better)
Ease the navigation of your site
Navigation is very important for search engines
The navigability of a website is important as it helps users to quickly find the content they want.
In addition, it can help search engines understand what content Webmasters think is important.
And although Google search results are offered at the page level, Google also likes to know the role a page plays within a website.
Plan the navigation based on the home page
All websites have a home page or root page, which is the most commonly visited website, as well as the starting point for many users.
Unless your site has only a few pages, you should think about how users will go from the general page (your root page) to another page that hosts more specific content.
Do you have enough pages on a certain topic to create a page that describes them?
Do you have hundreds of products that need to be classified into several categories and subcategories?
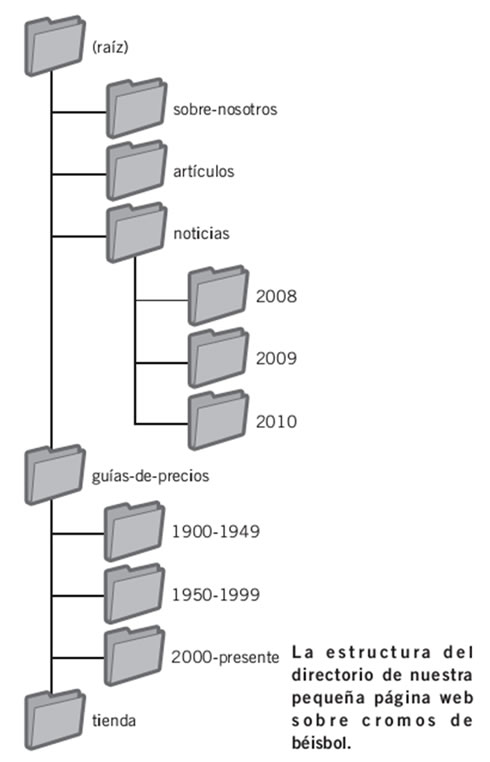
Make sure you use the navigation links
The links are a line of internal links located at the top or bottom and that allows users to go to previously visited sections or the home page.

The navigation links in an internal article of our website.
Many of these lines have the most general page (usually the home page) in first position and the more specific sections on the right.
Leave open the possibility that a part of the URL can be deleted
Think what can happen when a user removes part of one of your URL.
Some users may browse your website in very rare ways and you should anticipate this.
For example, instead of using the navigation links on the page, a user could remove part of a URL to find more general content.
He or she could be visiting http://www.brandonsbaseballcards.com/noticias/2010/eventos-béisbol-cromos.html, but type http://www.brandonsbaseballcards.com/noticias/2010/ in the navigation bar, Believing that this will show you all the news of 2010..
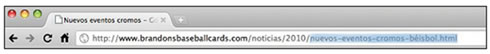
Users can access a higher directory by deleting part of the URL.
Is your website ready to show content when this happens or will it offer a 404 error ("page not found") to the user?
How about uploading the directory level to http://www.brandonsbaseballcards.com/noticias/?
Create two sitemaps: one for users and one for search engines
A site map is a normal and current page of our website in which its structure is shown, and which normally consists of a hierarchical list of the pages that comprise it.
Users may visit this page if they can not find a specific page of our website, although search engines may also visit this page for better indexing of the pages. This page is created primarily for users.
An XML sitemap file, which can be sent through the Google Webmaster tools, makes it easier for Google to find the pages of your website.
Using a sitemap file is also a way to tell Google, but not guarantee, which version of a URL you prefer as the main one.
Ease navigation on your website
Recommended practices
Create a hierarchy that flows naturally
Make it as easy as possible for users to go from the most general content to a more specific one within your website. Add pages that facilitate navigation when it makes sense to do so and link them effectively in the internal structure of links.
Avoid:
- Create complicated navigation links, for example, linking each of the web pages of your site with the rest
- Structure the content too much (so that it takes twenty clicks to get to the last content)
Use text for the navigation bar
Using text links in the navigation bar of your website makes it easier for search engines to track and understand it. Many users also prefer this type because some devices are not compatible with Flash or Java.
Avoid:
- A navigation bar containing only drop-down menus, images and animations
Many, but not all, search engines can find such links. However, if a user can access all the pages of a site through text links, this would improve the accessibility of your site.

Recommended practices
Add a HTML site map to the website and use a XML sitemap file
A simple site map with links to the rest of the pages or at least the most important ones.
Creating an XML sitemap file for your website will help make sure that search engines find the pages of your website.
Avoid:
- Make your HTML site map obsolete with broken links
- Create a HTML site map that is simply a list of pages without organization, instead structure them by topic
Create a useful 404 page
Sometimes users’ access, or because they follow a broken link or because they write a wrong URL, to pages that do not exist on your website.
Having a personalized 404 page that kindly guides users to a running page can greatly improve the user experience.
Your 404 page could have a link to the homepage and could even offer a series of links to popular pages or related content on your website.
Avoid:
- That your 404 pages are indexed by the search engines (make sure your web server is configured to give an HTTP 404 code when asking for pages that do not exist)
- Offer only vague messages such as "Not Found", "404" or not even a 404
- Use a design for your 404 pages that is not consistent with the design of your website
Providing content and quality services
Interesting sites will increase your value for yourself
Creating interesting and useful content will probably be what most influences your website of all the factors that were previously discussed.
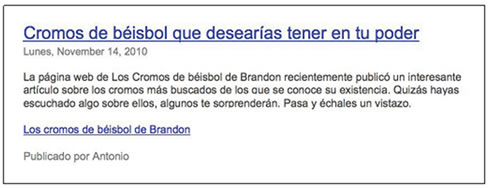
A blogger finds part of your content and then refers to it in an article.
Users recognize good content as soon as they see it and are likely to want to share it with other users. This can be through a blog post, social networks, email, forums or other means.
Organic content or word of mouth will be the most helpful in building your reputation with both users and Google, and this rarely happens without good content.
Anticipate the difference of knowledge of your users on the subject you are dealing with and offer unique and exclusive content.
Think of the words that a user could use in the search to find your content. Users who know a lot about the subject could use different words than others to whom the subject is new.
Anticipating these differences in how users do the searches and taking them into account when writing your content (using a good mix of keywords) can give good results.
So think well about creating a new and useful service that other sites do not offer.
You can also think about writing a research document that has not been dealt with before, be the first to publish news, or take advantage of the number of unique users you have.
Other websites may lack resources or experience in doing some of these things.

Recommended practices
Write easy-to-read texts
Users enjoy content that is well written and easy to understand.
Avoid:
- Write careless texts with many spelling and grammatical errors
- Incorporate text in image format when you want that text to be part of the content, since users may want to copy and paste the text, and also the search engines cannot read it
Focus on the topic
It is always beneficial to organize the content in such a way that the user has a good idea of where it starts, where a topic ends and where the next one begins.
Dividing your content into logical snippets helps users find what they want in a faster way.
Avoid:
- Put a large amount of text that covers several topics on the same page without paragraphs, headings or without a design that separates them
Create unique and original content
New content will not only make the users you already have go back to your website, but it will also attract new visitors.
Avoid:
- Redo (or copy) content that already exists, it will provide very little added value to users
- Have duplicate or very similar versions on your website
Create content primarily for users, not for search engines
Design your site according to the needs of users and if you also make sure that your site is accessible to search engines easily, you will have very good results.
Avoid:
- Insert a large number of keywords directed to the search engines, but they do not make sense and are annoying for users
- Have text blocks type "frequent misspellings used to reach this page" and offer little value to users
- Hidden text for users, but visible to search engines
Write better quality anchor text
Good anchor texts convey the content we're talking about better
The anchor text is that text that we can click on and that users see as a link. This is located on the anchor tag <a href="..."></a>.

This anchor text adequately describes the content of one of the articles.
The text tells users and Google something about the page to which it is linked.
The links on your web page may be internal, that is, linked to other pages of your website, or outgoing, that take you to content on other websites.
In both cases, the better your anchor text is, the easier it will be for users to get around your page and the easier it will be for Google to understand what the page to which you are linking is about.
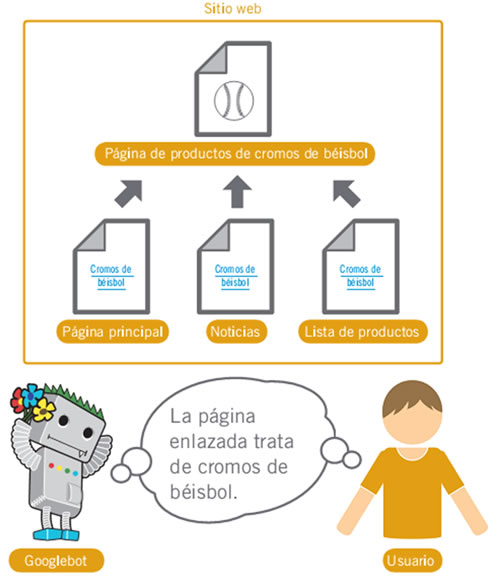
With proper anchor text, users and search engines can easily understand what the linked page contains.

Recommended practices
Choose a descriptive text
The anchor text that you use to link should offer at least a general idea of what the page to which you are linking is about.
Avoid:
- Write generic anchor text such as "page", "article" or "click here"
- Use text out of context or that is not related to the page to which it is linked
- Use the URL of the page as anchor text as a rule (although there are some legitimate uses, such as when, for example, you want to promote or refer to a new website)
Write concise texts
Try to write short and descriptive texts, usually with several words or a short phrase.
Avoid:
- Write long anchor text, such as a long sentence or a short paragraph
Format the links to make them easier to see
Facilitates users to distinguish normal text and anchor text from links.
Your content will be less useful if users do not find the links or click by mistake.
Avoid:
- Use CSS or a text format that makes links look like normal text
Use anchor text also for internal links
We usually think of links in terms of links to external pages, but if you pay more attention to the anchor text that we use for internal links this could help users and Google navigate better through your site Web.
Avoid:
- Use stuffing keywords too long or too long just thinking about the search engines
- Create unnecessary links that do not serve for users to browse the website
Optimize the use of images
Use the "ALT" attribute to provide information about the images
Images may seem like a very simple component of your website, but you can optimize your use.
All images can have a defined file name and an "alt" attribute, which we can take advantage of.
The "alt" attribute allows you to specify text that may appear instead of the image, if it cannot be displayed for whatever reason.

This image is not shown to the user for any reason, but at least the text in "alt" is displayed.
Why use this attribute?
If a user is viewing your Web page with a browser that is not compatible with the images, or is using alternative technologies, such as a screen reader, the content of the "alt" attribute will provide information about the image.
Another reason is that if we use an image as a link, the text in "alt" will be treated similar to an anchor text in a link text.
However, it is not recommended to use too many images as links in your navigation bar, when text links may work.
Finally, optimizing the file name of your images and the text in "alt" makes it easier to understand your images for image search results.
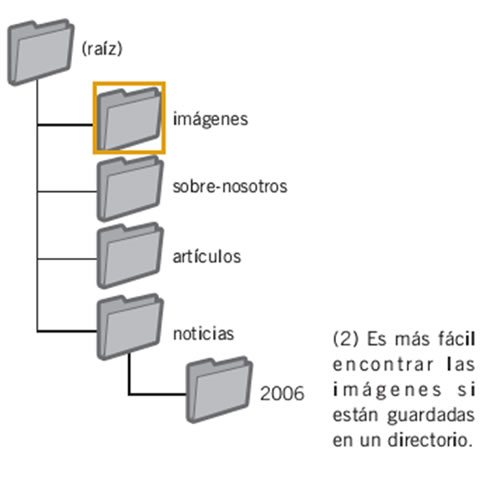
Save the files in specialized directories and work with them using standard file formats
Instead of having image files saved in different directories and subdirectories of your domain, consider regrouping your images in a single directory, for example, brandonsbaseballcards.com/images.
This simplifies the path of your images.
Use files that are widely accepted.
Most browsers support JPEG, GIF, PNG and BMP.
It is also a good idea that the extension that appears in the name of your files matches the type of the same.
Recommended practices
Use short and descriptive "alt" file and text names
As in any other part of the page that can be optimized, file names and "alt" text (for ASCII languages) work best when they are short and descriptive.
Avoid:
- Use generic names like "image1.jpg", "pic.gif" or "1.jpg" whenever possible (some websites with thousands of images may decide to give them the names of the images automatically)
- Write file names very long
- Fill the "alt" attribute with many keywords or copy and paste entire sentences
Offer "alt" text when you use the images as links
If you decide to use an image as a link, filling in the "alt" text will help Google understand more about the page you're linking to.
Imagine that you are writing the anchor text for a text link.
Avoid:
- Write long texts in "alt" that can be considered as spam
- Use only links in images to navigate through your page
Offer a file Sitemap of images
A file Sitemap of images can offer Googlebot more information about the images that are in your website.
The structure is similar to the XML Sitemap file of your Web pages.

Use header tags appropriately
Use head labels to emphasize an important text
Header tags (not to be confused with the HTML <head> tag or HTTP headers) are used to present the structure of the header. page to the users. These labels have six sizes, starting with <h1>, the most important, and ending with <h6>, the least important.

On the news page, we could put the name of our site on the <h1> tag and the news theme on <h2>
Since the tags usually make the text they contain larger than the rest of the page, this becomes a visual clue for users about the importance of that text and can help them understand about the type of content that is below it.
Different sizes of headers are used to create a hierarchical structure of your content, making it easier for users to navigate through the document.

Recommended practices
Imagine you are writing a scheme
This is similar to writing a scheme for a large project. Think on paper what are the main and secondary points of the content and then decide where to use the header tags appropriately.
Avoid:
- Place text in the header tags that would not help to define the structure of the page.
- Use header tags when other tags such as <em> and <strong> may be more appropriate
- Change header size to another without any logic
Use header tags sparingly
Use header tags when it makes sense. Too many header tags on a page can make users find it difficult to understand the content and see where one schema ends and the next begins.
Avoid:
- Excessive use of header tags on pages
- Putting all text on a page in a headerheader
- tag Usetags to format a text and not to present the structure of the page
Make effective use of the robots.txt
Restrict the trailers (bots) where it is not necessary with the robots.txt
The "robots.txt" file tells search engines which part of your site they can access and consequently track.

The robots of any search engine (marked with the asterisk character) that follow the rules should not access or crawl the content under the /images /directory or any URL that starts with /search
This file should be called "robots.txt", and it has to be in the root directory of your site.
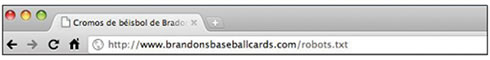
The address of our robots.txt file
There may be some pages on your site that you do not want to be crawled if they are not going to be useful for users when they find them in the search results.
If you want to prevent search engines from crawling your pages, Google Webmaster Tools has a simple robots.txt generator to help you create the file.
Keep in mind that if your site uses subdomain and you want some pages not to be crawled for that subdomain, you will have to create a robots.txt file specific to that subdomain.
There are a few more ways to prevent your content from appearing in search results, such as adding the "NOINDEX" meta tag, using .htaccess to protect directories with a password, or using Google Webmaster tools to remove content that has already been been tracked.

Recommended practices
Use safer methods for sensitive content
You should not stay quiet blocking only with sensitive or sensitive material.
One of the reasons is because the search engines could still refer to those URLs that are blocked (showing only the URL, without title or description) if there are links to those URLs somewhere in the Internet (registration of senders-referrer logs- ).
Also, search engines that do not follow Robots Exclusion Standard rules may disobey the instructions in your robots.txt.
Finally, a curious user could study the directories and subdomains in your robots.txt and guess the URL of the content that you do not want to be seen.
There are safer alternatives such as encrypting content or protecting it with a password in .htaccess.
Avoid:
- Allow to track pages of similar search results
- Users do not like to leave a search results page to reach another page that does not add any value
- Allow trace URLs created as a result of proxy services
Keep in mind rel="nofollow" for links
Combat span comments with "nofollow"
Setting the value of the" rel "attribute of a link to" nofollow "tells Google that some links on your site should not be followed or pass the reputation of your site to the pages with which you link.
Putting "nofollow" to a link is achieved using rel="nofollow" inside the anchor tag.
If you enter a link to a site that you do not trust or do not want to pass on your reputation, do not forget to use nofollow.
What can this serve?
If your site has a blog with public comments activated, the links of those comments can pass your credibility to pages that you would not feel comfortable linking to yourself.
The comment pages on blogs are very susceptible to receiving spam comments.

A spammer leaves a comment in one of our last posts trying to take away some reputation from our site.
Using nofollow in these links added by users assures you that you are not giving part of your very successful reputation to a spam site.
Add automatically "nofollow" to the colums of comments and to the message boards
Many software packages for blogs automatically add this attribute to user comments, but it is very likely that you can add these settings manually to those links that do not.
This advice also refers to any part of your site that accepts content generated by users, such as visitor books, forums, etc.
If you are willing to give credit to the links added by third parties (for example, if you trust a user of your site), then you do not need to use nofollow in the links.
Anyway, linking to sites that Google considers spam can affect the reputation of your site.
Another tip is to use CAPTCHA (distorted images or encrypted letters) and activate comment moderation.

An example of CAPTCHA. It can be a challenge to try to make sure that a person is leaving a comment.
Use "nofollow" for individual pages, all domain, etc.
If you are interested in putting "nofollow" in all the links of a page, you can use "nofollow" in the meta tag "robots", which is included in the <head> tag of the HTML code of that page.

This does not follow any link on a page
The way to write it is like this:
<meta name="robots" content="nofollow" />

Tell Google about your mobile sites
Configure your mobile sites so that they can be indexed with precision
Mobile communication is experiencing a moment of great boom. Many people use the mobile phone daily. However, as a Webmaster, running a mobile site and attracting mobile users is not that easy.
Mobile sites not only use a different format than normal sites, but the management methods and experience required are also different.
This gives rise to new challenges. Although many mobile sites are designed primarily with visuals in mobile, they have not been designed for search engines.
Here are some recommendations for solving problems that can help your site to be crawled and indexed correctly.
Make sure your mobile site is indexed by Google.
If your website does not appear in the search results Google mobile even using the operator site, is possible that your site has any of the following problems or both:
- Is possible that Googlebot cannot find your site. It is necessary that the Google robot crawls your site before it can be included in our search index. If you just created the site, it may still not be detected. In this case, create a mobile sitemap and send it to Google to inform about the existence of the site
- It is possible that Google's robot cannot access your site. Some mobile sites reject access to any device other than a mobile phone, which makes it impossible for Google's robot to access it and, therefore, makes your site can not be found. The Google crawler for mobile sites is "Googlebot-Mobile". If you want your site to be tracked, you must allow all User-agents, including "Googlebot-Mobile", to access your site. You should also bear in mind that Google can change the data of your User-agent at any time and without prior notice, so we do not recommend checking only if the User-agent exactly matches "Googlebot-Mobile". Instead, check that the header contains the "Google-Mobile" character string

An example of a mobile site that does not allow access to mobile devices. Remember that you must allow access to the User-agents, including "Googlebot-Mobile".
Check that Google can recognize your mobile URLs
Once "Googlebot-Mobile" tracks your URLs, check that each of your URLs is visually on a mobile device.
Pages that the robot believes cannot be viewed on a mobile phone are not included in the mobile site index. (although these can be included in the index of conventional Web sites).
This decision is based on different factors; one of them is the declaration of the "DTD (definition of type of document)".
Check that the DTD declaration of your URLs, adapted for mobile, had an appropriate format for them, such as XHTML Mobile or Compact HTML.

An example of DTD for mobile devices.
If the format is compatible, then the page is eligible to be included in the mobile search index.

Promote your site in the right way
Increase the number of incoming links with the intention to add value to your website
Although most of the links to your site will come gradually as people discover your content through searches or other sources and link to your page, Google understands that you want to publicize all the effort you have put into your content.
The effective promotion of new content has as a consequence a faster dissemination of your work to those who are interested in the subject.
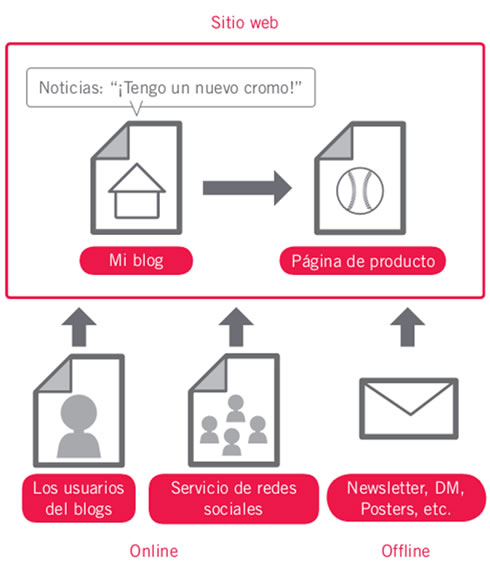
Promote your website and have quality links can lead to increase the reputation of your website.
Taking these recommendations to extremes could even damage the prestige of your site.
How to send notices through blogs and be recognized online
To publicize new services or content that you have on your site, a good idea is to write an article about it on your own blog.
Other Webmasters who follow your site or are subscribed with an RSS feed will also find out.
Putting some effort into the promotion off the Internet can be very helpful too.
For example, if you have a website for your business, make sure that the URL appears on the business cards, the header of your letters, etc.
They can also send periodic newsletters to your customers to let them know new content on the company's page.
If you run a local business, adding the information from it to Google Places will help you contact customers in Google Maps and Web search.
Recommended practices
Know the social networking sites
There are sites that have been built on the basis of the interaction between users and that have allowed people interested in certain topics to be contacted with relevant content.
Avoid:
- Promote every little addition you make; Do it only for bigger and more interesting things
- Engage in programs where your content is artificially promoted
Try to reach those who are in a community close to yours
There are many chances that there are sites that talk about the same topics as you.
Establishing communication channels with these sites is usually beneficial.
Current topics that appear in your community can give you ideas to write content or make a collection of useful resources.
Avoid:
- Send massive requests (spam) to all the sites that share the theme
- Buy links from another site in order to increase your PageRank instead of traffic

Source: Google, Tools for Webmaster
CITE ARTICLE
For homework, research, thesis, books, magazines, blogs or academic articles
APA Format Reference:
Delgado, Hugo. (2019).
SEO Google - Optimization Guide in Web Search Engines.
Retrieved Nov 18, 2025, from
https://disenowebakus.net/en/search-engine-optimization





