Methodology for the Creation and Development of Websites
The elaboration of Web pages includes the phases of Analysis, Planning, Content, Design, Programming, Testing, Marketing and Advertising.

The "Methodology for Web Site Creation" incorporates the steps of Analysis, Planning, Content, Design, Programming, Testing, Marketing and Advertising
The article talks about:
Analysis
When developing a Website you shouldbeginto respond to a very specificset of questions that will basically clarify and define the existing expectations around the Web application and interaction that will be generated.
Such questions might include:
- Is the Web site is really needed?
- For what the website is needed?
- What the users on the website are looking for?
- What image you want to project with the Web site to the users?
- What interactive services will be integrated through the website?
- What resources are available for the development of the website?
- How much time should be invested in the development of the website?
- What impact the Web site will cause to the users?
Selection of Objectives
All projects must have defined objectives, against which can be measured the effectiveness of the actions developed.
Green, Chilcoott and Flick (2003) called this stage, summary of objectives, which set out three key points for this selection, which are to:
- Define the users
- What users expect from the visit
- What pretends to communicate through the Web site
We can also name them: user selection, user expectations and expectations of the organization; It described below:
User selection
Users or audience refers to that part of the population that is to be achieved or influence with the website; this is closely linked to the nature of the proposed site.All information obtained will be used to establish part of the:
- Criteria of content design
- Languages
- Aesthetics
- Among others
"The user modeling is based on defining user classes or profiles and like that design in order to satisfy the own needs of each user group"
User expectations
The organization may or may not be known to potential users of the site. When considering the launch of a website it is necessary to know to whom it is addressed and what the users could expect visiting it.
"Take a time to connect with your customers, suppliers and friends, in order to figure out how they would do to find your website and what they would like to see in it."
Organizational expectations
It is vital to establish or fix what results the organization intends to achieve with the creation of the Web site. With that it seeks to define the purpose of your website, and should include aspects ranging from the most general, related to the target audience, to the more specific related to the organization.
Morrin and Dickson (2001) indicate that you must decide if you are looking to the Web site is:
- Increase sales
- Offer specialized services and expertise
- Advertising and sponsorship
- Incentives (free products for promotion)
- Publicize
Planification phase
Every project has a planning phase. It must define:
- What are the technical requirements for this purpose
- Who the team members will be
- Select the structure
- Plan a well organized site
- Perform studies of comparative marketing
Software selection
At this stage of the methodology it seeks to determine the requirements in terms of the software to be used for application development; i.e., :
- Operating systems
- Server (software)
- Web design editors
- Programming languages
- Animations and other components
This definition will depend on many aspects such as the existence of software licenses or hardware and technical resources.
Hardware selection
Before undertaking the development of a Web application, you must determine the:
- Hardware requirements of the application
- The server equipment
- Answer capacity
- Terminals
- Network requirements if the application must be available on an intranet or extranet
In the case that the application will be published on the Internet, the domain should be reserved andlocate the hosting service of companies that specialize in this service (Morrison and Dickinson).
Selecting the right equipment
"The teamwork environment originates from the need to segment the production process in several different functions"
Part of a Web site planification is to think in terms of teamwork.
It is about the set of technicians who will be responsible for the creation, construction, evaluation and maintenance of the site.
The team will be based on the convergence of knowledge and experiences. It must be composed of technicians from many different disciplines, able to contemplate the various aspects at stake.
Initially, most of the organizations had in charge of the website a Webmaster who worked alone, preparing the server, edited pages, did graphic design, and wrote or reunited the texts. Over time, the complexity of these projects was understood.
It is very important that the team has a leader (which may in the future be the Webmaster or not) because forming a Web team requires a great personal and institutional commitment.
The teams are not built for the overnight, or from an administrative decision or a mandate. They require a process of consolidation, which runs through search times, agreements and adequacy.
A Web team should be in constant communication with both who have assigned their mission, as with their recipients (customers or users). Its success is also based on close colaboration and communication between its members.
Each member of the Web team should be trained in their field of work (the presence or level of experience of certain members of the team can vary depending on the project).
A list of members who could be part of this teamis suggested:
- Project Manager: Responsible for the supervision and control of the rest of the team. It acts as a link between the user and the other members
- Producer: This is responsible for setting the appearance, perception and functionality of the site
- Editor: Helps to establish and maintain the style, in addition to the integrity of the site. It is responsible for the control of the correction and text flow and in some cases the multimedia content on the site
- Writer: Writers should be interested in the technical details and the incorporation of development standards with the site, using the right words, spelling and grammar. It is necessary that the writer has knowledge of HTML, or tools with FrontPage or other application
- Database Designer: Develop databases that manages the Web site, it is responsible for defining their relationships
- Script Designer: Works along with the database designer. Develops and debugs the scripts, ActiveX components and other interactive elements on the Web
- Graphic Designer: Responsible for creating the visual site files, can also be responsible for creating audio and movie files. Works with images and small programming tasks
- Hardware Technician: Configures, tests, operates and maintains computers, printers and necessary for the implementation and maintenance of site machines
- Tester: If there’s a large or complex site incorporating a test technician to theteam can be beneficial. Their job is to ensure that everything works as it should, it is responsible for testing the elements of all pages
Although these functions could be taken as essential, the structure will always be determined by the scope of the project.
Benchmarking
It is a way to detail, monitor and evaluate all those Web pages rated as the best that is in the network, in order to design a way that allows the creation of a product of high quality, productivity and competitiveness.
A practical way of performing benchmarking is propose a series of questions when visiting the sites that were selected as the best in the industry, Morris and Dickson (2002) suggest the following:
- What are the objectives of the site?
- How long does it take to load?
- Did it load in a logical order?
- Is an interesting website?
- How are the graphics?
- Does it reflect the gender of the business or company?
- It is easy to use and is comfortable navigating it?
- Is the content is structured logically?
- Are there too many or insufficient levels of information?
- In general, is the site a success?
Navigation structure
“The basis of a well-designed site is a precisely defined structure”
The relations of pages between themconfigure the site structure.
These are linked from the home page by links to the rest of pages, this is pretty simple using HTML, but is more difficult to decide the order, how and with what settings links will be established.
The structure of a Web page is very important as it will allow the reader to visualize all the contents in an easy and clear way (good structure) or make to the reader a sense of being lost, which will not quickly find what is seeking and eventually will abandon the site (poor structure).
Green, Chilcott and Flick (2003), highlight the types of navigation structures:
Linear structure
This structure consists of a straight line that runs through the site from the home page to the final page.
It is very useful when you want the reader to follow a fixed and guided path, and to prevent getting distracted by links to other pages. On the other hand it can cause to the reader the feeling of being trapped if the road is very long or uninteresting.
This type of structure would apply to learning tutorials or guided visit tours.

Hierarchical structure
The hierarchical structure, as shown in the following figure:
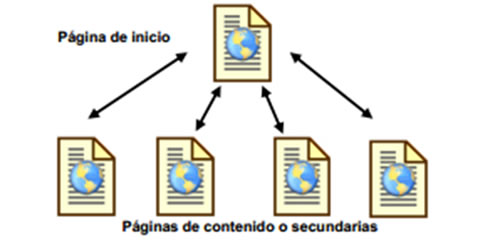
It is the typical tree structure, in which the root is the welcome page, it can also be replaced by the content, in which the different sections containing the site are exposed.
The advantage of this structure is that the user is always located and can easily move around the site.
Because the majority of secondary pages allow the return to the homepage, visitors fully control the navigation.
Radial structure
In this model the secondary pages are not connected to each other, and must navigate through the home page to go from a secondary to another, i.e., the main page contains links to all secondary, but secondary only contain an environment to home, as is shown in the figure below:

The advantage of this structure is that it facilitates navigation, visitors will have to make only one or two clicks to return to the main page; However, this could also be a disadvantage because it forces the user to always return to the homepage.
Network structure
Here a model in which all pages are interrelated is proposed. It is an ideal structure for specialized sites on a topic in which the user is allowed free navigation without limitations as we see below:
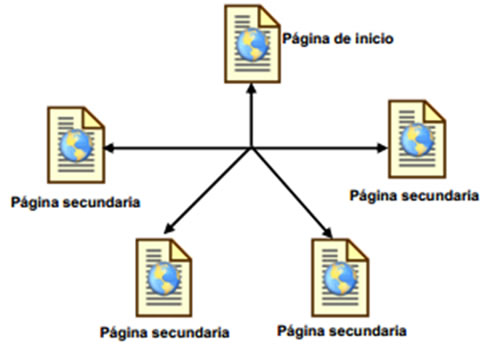
Investment costs
When planning a Web site, you must perform a feasibility study that reflects the financial cost to invest, and that includes: time, personnel, Web hosting, domain, licenses if needed and maintenance:
- Time
- Personnel
- Web hosting
- Domain
- Licenses if needed
- Maintenance
Having a time control method becomes relevant in Web development, as in other projects, as time involves money.
A technique for controlling the cost of certain activity, is the agenda system, which consists individe each hourinto six minute segments called units, and it’s from the amount of units per activity in which the cost will be measured.
Benefits to obtain
The launch of the site is not everything, planning the development of a Web site needs to includeaspects such a benefits toacquire with the operation.
Prior to establishing the development of a Web site you should estimate the time of return on investment, in a tangible form, such as a monetary return, or intangible such as improving interpersonal relationships of the organization.
Content phase
The success of a Web site is mainly because of its content. The content is probably a combination of the information currently owned and the information to create.
It is convenient to show a content according to the planned objectives to develop the site, and the information to express covers the needs and interests of the public to whom it is addressed.
Design phase
Web design involves extensive and detailed work, since it covers not only the interaction of multiple elements, such as multimedia technology (audio, sound, images, animations, etc.); but also it covers integration with a logical structure based on the site's purpose.
Representing a task that goes beyond the simple needs and concerns of potential users.
When designing Web sites, it is necessary to take into consideration aspects such as usability and accessibility.
Usability
Referred to the time, effort and required by the visitor in order to attain a certain level of adaptation to the system, this can sometimes be linked to the number of steps required to achieve certain activity, and the level of knowledge required for users for the application usage.
Accessibility
A Website is developed with the idea that it must be seen by the largest number of visitors, but keep in mind that each of these can access information with different computers, browsers, and languages, these factors may prevent the site to be fully appreciated.
Romero (1999) identifies three key areas to determine the accessibility of a Web site, these are:
- Accessibility to the computer: Referred to the ability of hardware which it must have to use the Web application, the ideal in this area is that the application adapts to any computer
- Accessibility of used browser:Occasionally same contents are displayed differently in different Web browsers, is recommended using a design that can be viewed in most browsers and attached to standards
- Web page design accessibility: Users may have disabled some features of Web browsers, which could affect the proper display of the contents of the Website
Programming phase
This step corresponds to the use of Web programming tools. At this point it is essential to select:
- The programming languages in which the Website is developed
- The database defines
- Which content will be static and what will be dynamic
Once these criteria is defined it’s passed to a stage known as three phasesarchitecture, which states:
- Databases: It designs and creates the database
- Intermediate Programming: Programs or code that will run on the Web server. Here the communication between the database and the interface will be set
- Interface: Programs and codes that will deploy the content to users through the Web browser. It is referred to applications that the user will see andopérate through it
Testing phase
Extensive tests are run to ensure perfect operation of the Web site to users who will use the site:
- Checking in browsers:The first and most important step is to check that the pages can be viewed correctly in different browsers
- Detect broken links: It is necessary to detect documents that exist in the site but that are not connected by links; they must be repaired or removed if not needed since they’re taking up space on the server and tend to create confusion
- Check download times: One of the key points in the success of a website is its download speed, based on this it’s recommended a minimum download time
Here managers should receive training to develop their tasks.
Market and advertising phase
This phase should take into consideration the International Copyrights, whereby:
- All copies include copyright
- Developers credits or a link that allow users to contact them is appended
The site domain is then defined, verified that it is available to register, and files to the remote FTP server or from the server page are transferred. You must verify that all the files are in the corresponding folder of the Web.
After publication of the Web, diffusion depends onthe publicity given by the organization’s stationery from banners on specific sites through search engines and others.
CITE ARTICLE
For homework, research, thesis, books, magazines, blogs or academic articles
APA Format Reference:
Delgado, Hugo. (2019).
Methodology for the Creation and Development of Websites.
Retrieved Nov 11, 2025, from
https://disenowebakus.net/en/methodology-web-site-creation