History and evolution of the Internet. How the Web was born
The history of the internet began more than three decades ago when the scientific community was looking a way to share information.

The history of the internet began three decades ago, when the scientific community was looking a quick and effective way to share information, knowledge and success.
Then man has always recopilated and kept information.
The emergence of computers led to the origin of the open platform where they exchanged structured documents in a reliable and universal way.
The computers were linked to each other to store information between universities, defense organizations and government sites but, they did not have a common standard to communicate with, the information did not pass between different systems.
The connection between systems and the transfer of documents or data was a problem.
In this context, at the end of the 60s ARPAnet (Advanced Research Projects Agency) was created, which made available to scientists an analogous network called NSFnet, created by the NSF (National Science Foundation).

This network allowed communication between many universities and developed a new communication system to develop protocols called "packet switching".
In this system the data messages were transmitted in different packages, each with information about error control.
These packages could take different paths depending on the saturation of the network, and redo when arriving at the destination. This is how the networks began to grow.
That network of data transmission had in principle strictly military objectives, aimed at maintaining communication at any price in the event of a nuclear attack. Its creation immediately attracted the attention of professionals from around the world.
In the 70s appeared the Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP / IP), which based Internet services and email messages.

The standards developed in that period passed in the 1980s to the Defense Communication Agency of the Department of Defense of the United States, which became its guardian until they switched to the Internet Architecture Board when the Internet boom was born.
At the end of the eighties, the number of users that were connected to the network grew significantly and, more importantly, began to internationalize.
Then the use of the network was limited to exchanging emails and to have a global library with the most up-to-date information on the planet. Identifying and locating certain information was a difficult task.
The possibility of connecting all the existing networks in the world began to be glimpsed, but to achieve this it was necessary to create a standard of storing the data that could be seen from any computer platform.
And so the Web arose, its inventor, the researcher Tim Berners-Lee.. Twit it
Who investigated how computers could store information with random links and proposed the idea of a global hypertext space in which any information could be accessible by the network could be referenced by means of a single Universal Document Identifier.

Tim Berners-Lee, the father of the web.
In 1989 from the CERN (Conseil Européen pour la Recherche Nucléaire, European Organization for Nuclear Research) based in Switzerland, Berners-Lee presented a software based on protocols that allowed to visualize the information using the hypertext.
These advances changed what could be done in a computer network, extending its scope to limits unknown until that moment.
With this kind of pseudo language it was possible to embed objects, such as images and videos, as well as references in the form of links; the well-known links, through which it is possible to view and access other documents, not only from the computer itself, but also from remote computers, and even generated and stored on different platforms.

HTML Hypertext Marking Language
Thus was born HTML (HyperText Markup Language or Hypertext Label Language), which would become the standard of Web design in the following years.
Other specifications were also developed such as URL and HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) published on the first server and achieved widespread dissemination.
These specifications spread quickly among professionals and between 1991 and 1994, the load on the first Web server info.cern.chaumented ten times each year.
Immediately a group of students from Illinois University, including Marc Andreessen, was dedicated to improving aspects of it, especially the addition of the GUI (Graphical User Interface) that served as the basis for adapting the language to the Microsoft Windows graphical environment

Marc Andreessen worked on HTML improvements
Then came a time of vertiginous and unstoppable growth. Several browsers were developed for different types of computers.
With the launch of the Mosaic browser by the NCSA (National Center for Supercomputing Applications) the network began to be accessible to all audiences.
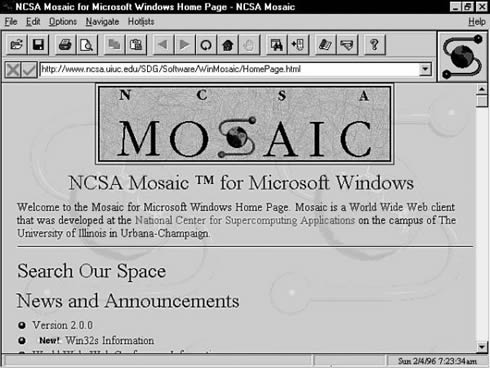
First Mosaic Web browser
Andreessen and other researchers founded the Netscape Communication Corporation that produced the first version of this browser, and Microsoft, not to be left behind, launched Microsoft Internet Explorer, initiating the so-called battle of the navigators for the dominance of the market, a phenomenon that it fostered the arbitrary appearance of non-standard forms of HTML.
Since then the Web has grown faster than any other known technological means.
To define a future direction, Tim Berners-Lee created the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) in 1994, www.w3.org, which since then acts as a neutral forum where companies and organizations can discuss and agree on new computer protocols.

W3C World Wide Web Consortium
This non-profit entity is financed by a significant number of corporate members, including the well-known Compaq, Microsoft, AOL, Sun and AT & T, among others.
Its main objective is to develop technological standards available to all, which guarantee the homogeneous growth of the Web. Among the best known is HTML itself, CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), XML (Extensible Markup Language) and DOM (Document Object Model).
The fact of working with standards facilitates to programmers and designers the necessary compatibility to create Web sites, dynamic, effective and downloadable from any device or platform.
Those technologies, developed in their origins in order to solve the basic needs of communication between military and scientists, served as the basis to create a special scenario that soon became the world's largest and most important mean of communication, cooperation and trade: The Internet.
CITE ARTICLE
For homework, research, thesis, books, magazines, blogs or academic articles
APA Format Reference:
Delgado, Hugo. (2019).
History and evolution of the Internet. How the Web was born.
Retrieved Nov 12, 2025, from
https://disenowebakus.net/en/internet-history






